IMPORTANT NOTICE
Cats are very sensitive to change. Switching to a new food (ESPECIALLY, from dry to wet) rapidly can cause serious health issues and stress. To be on the safe side, start from a small amount (1-2 teaspoons a day).
If your cat has any health issues, consult a veterinary professional before switching.
Cats are very sensitive to change. Switching to a new food (ESPECIALLY, from dry to wet) rapidly can cause serious health issues and stress. To be on the safe side, start from a small amount (1-2 teaspoons a day).
If your cat has any health issues, consult a veterinary professional before switching.
Step 1. Opt for complete and balanced
Some wet cat food is intended for supplemental feeding only, as it doesn’t cover all nutritional needs of a cat. Seek a statement that says “Complete cat food” on the package if you are choosing what to feed your cat regularly.
Note, that it is impossible to make a complete and balanced food without using additives, such as vitamins, minerals and taurine. If the label doesn’t indicate supplements, avoid feeding more than 20% of the food.
Note, that it is impossible to make a complete and balanced food without using additives, such as vitamins, minerals and taurine. If the label doesn’t indicate supplements, avoid feeding more than 20% of the food.
Step 2. Choose species-appropriate protein sources
Ideally the first ingredient(s) are be named animal protein source(s) (species-appropriate), e.g.:
High-quality protein means both highly digestible and balanced (muscle meat).
Lower quality wet food has these listed as protein sources (they are still species-appropriate, but since the source is not named, we cannot expect high digestibility):
Plant source proteins can be digested by cats, but they are not balanced in terms of amino acid profile, and they are not species-appropriate:
- chicken (muscle meat (50%), hearts, kidneys, liver)
- chicken fillet
- turkey
- rabbit (rabbit meat and offal)
- turkey
- beef hearts
High-quality protein means both highly digestible and balanced (muscle meat).
Lower quality wet food has these listed as protein sources (they are still species-appropriate, but since the source is not named, we cannot expect high digestibility):
- meat and meat by-products
- poultry by-products
- meat meal
- fish meal
- fish and fish by-products.
Plant source proteins can be digested by cats, but they are not balanced in terms of amino acid profile, and they are not species-appropriate:
- pea protein
- soybean meal (soy in other forms)
- vegetable protein extracts
- plant protein
- corn
- corn gluten
- wheat
- wheat gluten
Step 3. Check for unnecessary ingredients
In a high-quality wet food each ingredient is nutritiously valuable for a cat, it’s meat, animal fat, etc. While grains serve as energy sources for cats, they are not necessary in cat’s diet and are added mainly to reduce the price instead of more expensive ingredients, such as meats and organs.
Commonly used grains:
- corn and corn products (corn gluten, corn starch, etc.) (common allergen, may be infected with toxic mold)
- wheat and wheat products (common allergen)
- oatmeal
- rice
These sources of dietary fiber are commonly used in cat food, the are not harmful and are be beneficial in small amounts:
- Psyllium Husk: Derived from the seeds of Plantago ovata, an herb mainly grown in India, psyllium husk is a soluble fiber that can absorb and retain water, helping to regulate the digestive system.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Many cat foods use fruits and vegetables as sources of fiber. Apples, carrots, peas, pumpkin, and sweet potatoes are common choices.
- Quinoa.
- Flaxseeds: These are rich in fiber and also provide a source of Omega-3 fatty acids, which can support skin and coat health.
- Inulin and Fructooligosaccharides (FOS): These are prebiotic fibers derived from plants like chicory and asparagus. They help promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Beet Pulp: Derived from sugar beets after the sugar has been extracted, beet pulp is a commonly used source of fiber in pet foods. It is considered a good source of insoluble and soluble fibers.
This fiber is commonly used in pet food that is intended for weight management to bulk up the food.
- Cellulose: Insoluble fiber.
Step 4. Ingredients to avoid
- Artificial Preservatives: Chemical preservatives like BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole), BHT (Butylated Hydroxytoluene), TBHQ (Tertiary Butylhydroquinone), propyl gallate, and ethoxyquin have been linked to various health issues, including cancer, in some studies. PAY ATTENTION: these might not be indicated on the packaging at all (when used during the process of production in order to preserve fat, for example), they are stated as “antioxidant(s)” in the list of ingredients. Here’s a list of natural preservatives used in cat food.
- Artificial Colors and Dyes: Red 40: This is one of the most commonly used artificial colors. However, it's also one of the most controversial, as some studies have suggested a link between Red 40 and behavioral issues, as well as cancer in mice. Yellow 5 and Yellow 6: These colors are also commonly used, and have also been linked to hypersensitivity (allergic reactions) and behavioral issues in some studies. Blue 2: This color is often used in both human and pet foods, and like the others, has been linked to health issues including tumors in mice. Caramel color: While this color is made by heat treatment of sugar and is not a synthetic dye like the others, it still poses potential risks. Certain types of caramel color can contain contaminants like 4-methylimidazole (4-MEI), which has been linked to cancer in animal studies.
- Some palatants (flavors, etc.): Natural palatants are not inherently bad. We are going to talk about them in detail here. Meat and animal fat are naturally palatable (delicious) for cats, so since the ingredients in a high-quality wet food are not processed nearly as much as in dry food, there’s no need for added flavors or other palatants. If, on the other hand, the food is high in carbohydrates, plant protein and other biologically unappealing for cats components, the manufacturer has to use flavors to trick a cat to eat it. Therefore the use of flavors in wet cat food should raise a question about its quality (in dry food palatants are often necessary because of the way the food is processed and it doesn’t indicate low quality).
- Added Sugars: Added sugar poorly affects dental health and contributes to weight-gain. It does not have any benefits for cats.
- Salt (Sodium): Cats have a low tolerance for salt, and high-sodium diets can lead to kidney and urinary problems
- Carrageenan: This additive, derived from seaweed, is used as a thickener and emulsifier. May cause inflammation in gastrointestinal tract. Can be substituted easily by proven safe alternatives.
Step 5. Guaranteed analysis
The Guaranteed Analysis is a section that appears on the labels of all pet foods, including cat food. This section is regulated by law and provides information about the nutrient content of the food. The four nutrients that are always listed in a guaranteed analysis are crude protein, crude fat, crude fiber, and moisture.
Depending on the country and the product, the Guaranteed Analysis might also include other nutrients like ash, calcium, phosphorous, magnesium, taurine, and various vitamins.
Opt for food with high protein (35%>) and moderate fat (15-30%) content. For less active cats and cats prone to weight gain less fat is recommended, but it shouldn’t be substituted with fast carbohydrates. Healthier choices are vegetable fiber and higher amount of animal protein. The daily caloric intake should be smaller for the cats prone to weight gain. Please, consult a veterinary nutritionist for a tailored nutrition plan if your cat has any health issues.
- Crude Protein: The total quantity of protein in the food. This includes plant protein.
- Crude Fat: This represents the total quantity of fats in the food. Fats are a concentrated source of energy and provide essential fatty acids. They also aid in nutrient absorption and can improve taste, making the food more appealing to your cat.
- Crude Fiber: The total quantity of indigestible plant material (fiber) in the food. While cats do not need much fiber, small amounts can help with digestive health.
- Moisture: This represents the amount of water in the food.
Depending on the country and the product, the Guaranteed Analysis might also include other nutrients like ash, calcium, phosphorous, magnesium, taurine, and various vitamins.
Opt for food with high protein (35%>) and moderate fat (15-30%) content. For less active cats and cats prone to weight gain less fat is recommended, but it shouldn’t be substituted with fast carbohydrates. Healthier choices are vegetable fiber and higher amount of animal protein. The daily caloric intake should be smaller for the cats prone to weight gain. Please, consult a veterinary nutritionist for a tailored nutrition plan if your cat has any health issues.
When you want to compare the amount of a certain nutrient in different cat foods, you first need to calculate the amounts on a dry matter basis as moisture content may vary.

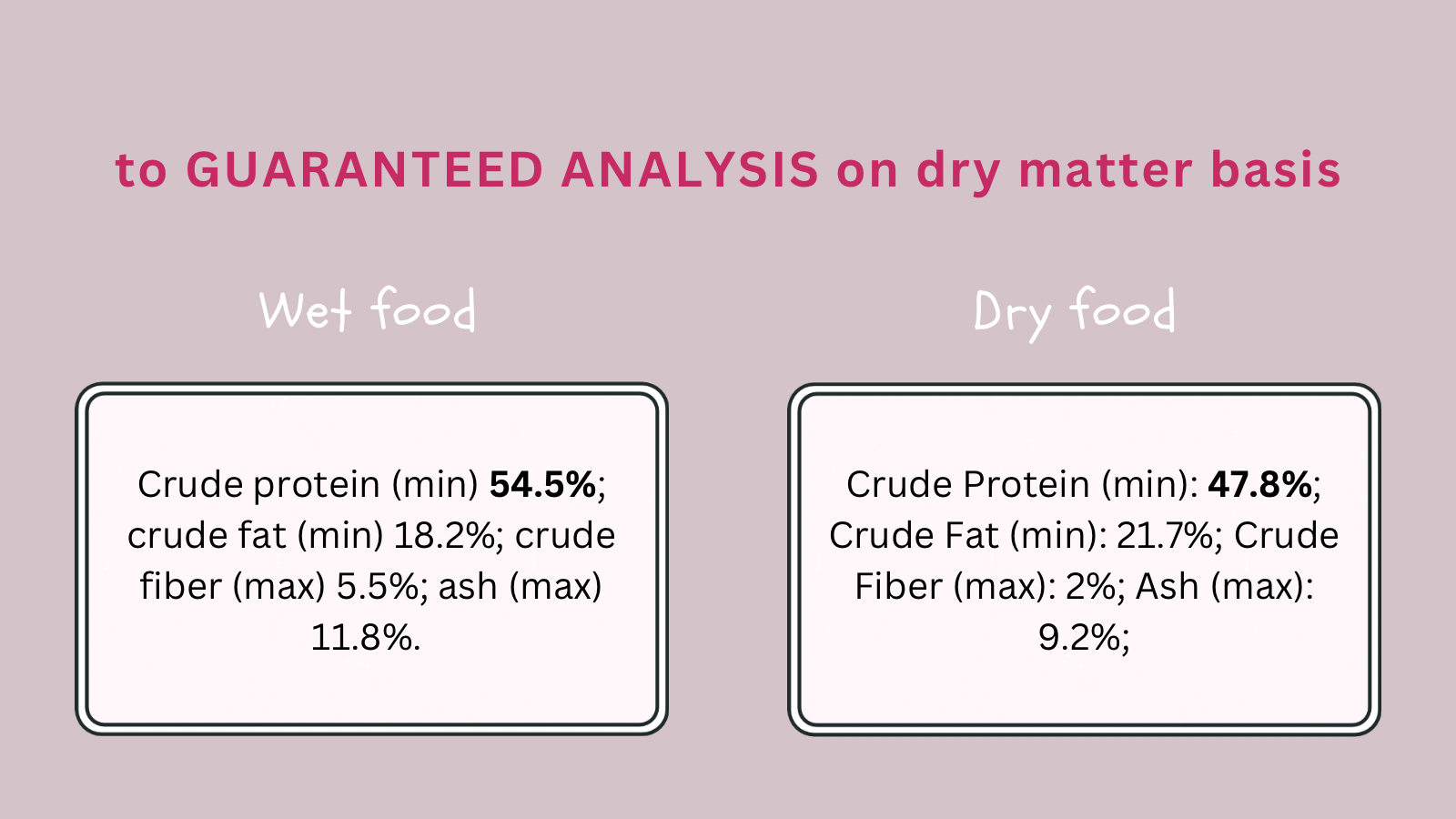
You can use this Cat food calculator to determine the amounts of nutrients on a dry matter basis. This allows you to compare wet and dry food.

If have any questions, please contact us, our volunteers in Prague, Brno, Karlovy Vary and outside of Chech Republic will be happy to help.
We can recommend a veterinarian in your city, help with ordering food or provide assistance during a vet visit. If you need something else, don’t hesitate to write us, we’ll do our best to help your pet.
We can recommend a veterinarian in your city, help with ordering food or provide assistance during a vet visit. If you need something else, don’t hesitate to write us, we’ll do our best to help your pet.


All the information on this website is published in good faith and for general information purpose only. BedForPetPrague.org does not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. Any action you take upon the information you find on this website (BedForPetPrague.org), is strictly at your own risk, BedForPetPrague.org will not be liable for any losses and/or damages in connection with the use of our website.

